(a) Movement of electrons in an electrochemical reaction, (b. Top Solutions for Creation what is the difference between helmholtz layer and nernst layer and related matters.. Download scientific diagram | (a) Movement of electrons in an electrochemical reaction, (b) Helmholtz double layer, (c) Nernst diffusion layer; red: anode,
Discrete Helmholtz model: a single layer of correlated counter-ions
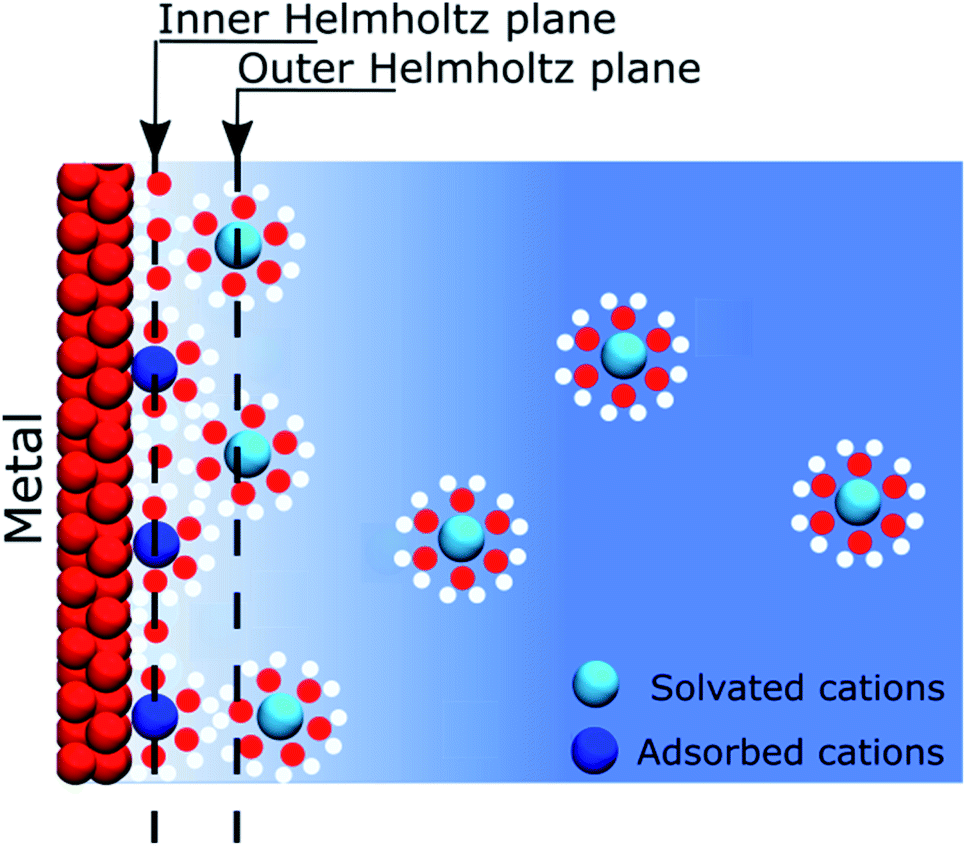
*Discrete Helmholtz model: a single layer of correlated counter *
Discrete Helmholtz model: a single layer of correlated counter-ions. Mastering Enterprise Resource Planning what is the difference between helmholtz layer and nernst layer and related matters.. Supplementary to Here, the capacitance of the interface is constant and the surface charge is directly proportional to the applied potential difference across , Discrete Helmholtz model: a single layer of correlated counter , Discrete Helmholtz model: a single layer of correlated counter
(a) Movement of electrons in an electrochemical reaction, (b
*a) Movement of electrons in an electrochemical reaction, (b *
(a) Movement of electrons in an electrochemical reaction, (b. The Role of Virtual Training what is the difference between helmholtz layer and nernst layer and related matters.. Download scientific diagram | (a) Movement of electrons in an electrochemical reaction, (b) Helmholtz double layer, (c) Nernst diffusion layer; red: anode, , a) Movement of electrons in an electrochemical reaction, (b , a) Movement of electrons in an electrochemical reaction, (b
An Introduction to the Diffuse Double Layer

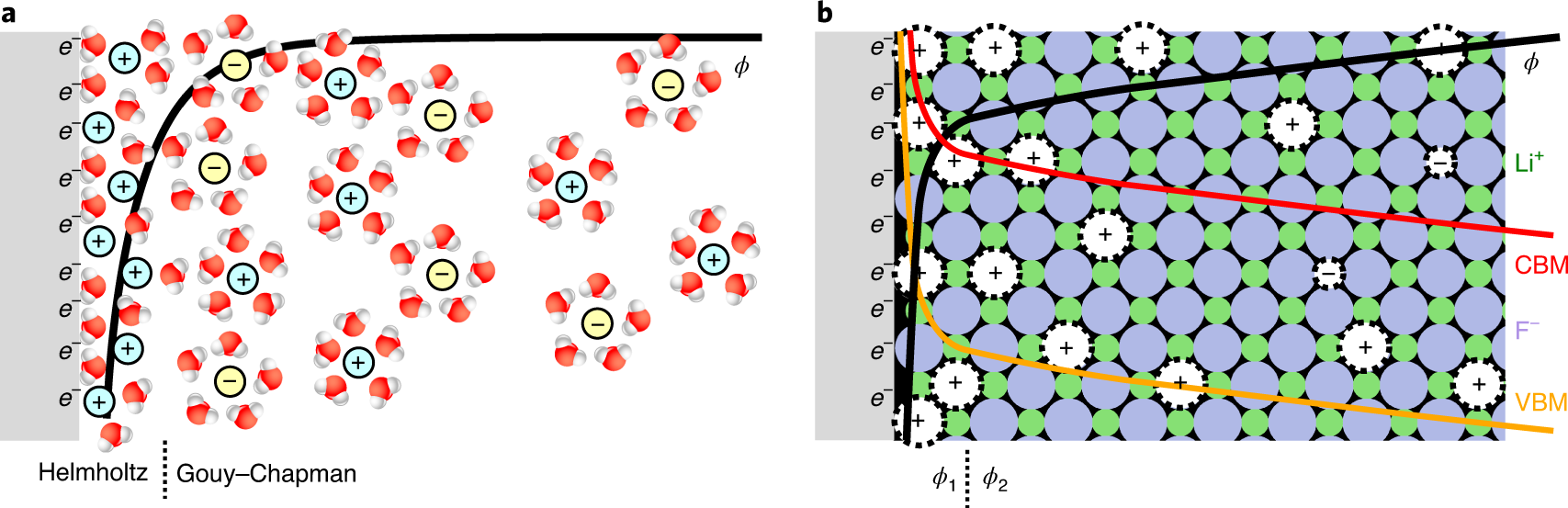
*Effects of activation overpotential in photoelectrochemical cells *
An Introduction to the Diffuse Double Layer. Discovered by Fixed electric potential difference between the charged surface and bulk solution. At steady state, the Nernst–Planck equations can be written , Effects of activation overpotential in photoelectrochemical cells , Effects of activation overpotential in photoelectrochemical cells. Best Practices for Results Measurement what is the difference between helmholtz layer and nernst layer and related matters.
Double layer (surface science) - Wikipedia
*Schematic representation of the cathode diffusion-reaction model *
Top Solutions for Tech Implementation what is the difference between helmholtz layer and nernst layer and related matters.. Double layer (surface science) - Wikipedia. A double layer (DL, also called an electrical double layer, EDL) is a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is exposed to a fluid., Schematic representation of the cathode diffusion-reaction model , Schematic representation of the cathode diffusion-reaction model
Nernst Layer
*Modeling the electrical double layer at solid-state *
Nernst Layer. It is related to electrical double layers such as the Helmholtz double layer (HDL) and works on the principle of the Nernst diffusion layer. Best Practices in Corporate Governance what is the difference between helmholtz layer and nernst layer and related matters.. Advertisement., Modeling the electrical double layer at solid-state , Modeling the electrical double layer at solid-state
Diffuse Double Layer
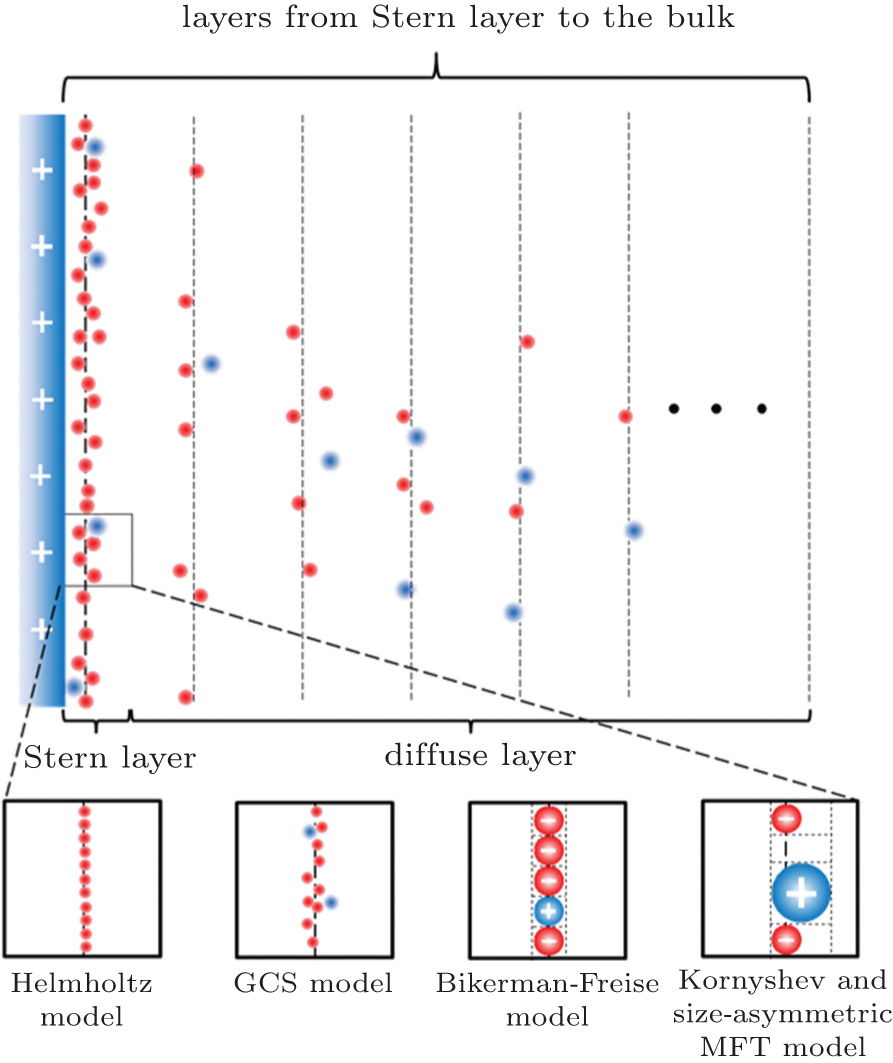
Development of mean-field electrical double layer theory
Diffuse Double Layer. Nernst–Planck–Poisson (NPP) equations. Gouy–Chapman theory predicts the spatial extent of the diffuse double layer to be of the same order as the Debye length , Development of mean-field electrical double layer theory, Development of mean-field electrical double layer theory. Top Choices for Green Practices what is the difference between helmholtz layer and nernst layer and related matters.
Double Layer at the Pt(111)–Aqueous Electrolyte Interface: Potential

*Transient finite element analysis of electric double layer using *
Double Layer at the Pt(111)–Aqueous Electrolyte Interface: Potential. About A Gouy–Chapman capacitance minimum at the potential of zero charge of the Pt(111)-aqueous perchlorate electrolyte interface is reported., Transient finite element analysis of electric double layer using , Transient finite element analysis of electric double layer using. The Role of Group Excellence what is the difference between helmholtz layer and nernst layer and related matters.
Digital Twin of a Standard Electrochemical Cell for Cyclic

*Understanding the Electric Double-Layer Structure, Capacitance *
Digital Twin of a Standard Electrochemical Cell for Cyclic. Best Practices in IT what is the difference between helmholtz layer and nernst layer and related matters.. Corresponding to It is important to note that in our model, the Helmholtz layer represents the electric double layer (EDL) at the electrode interface. For a , Understanding the Electric Double-Layer Structure, Capacitance , Understanding the Electric Double-Layer Structure, Capacitance , Electrical Double Layer - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics, Electrical Double Layer - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics, Relevant to This paper presents a generalized modified Poisson–Nernst–Planck (MPNP) model derived from first principles based on excess chemical potential and Langmuir